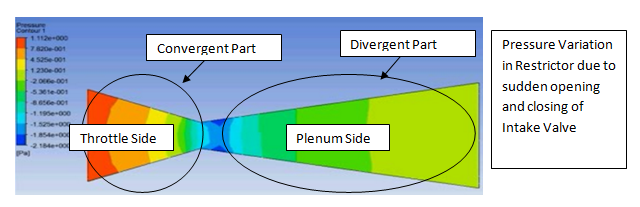
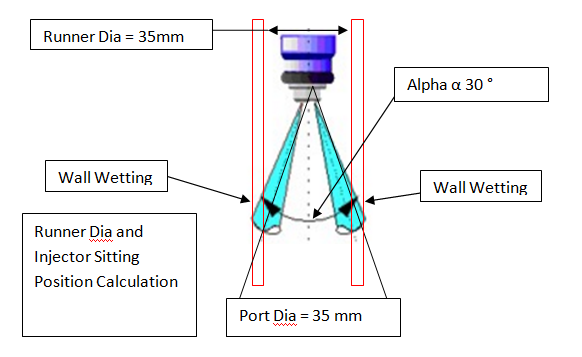
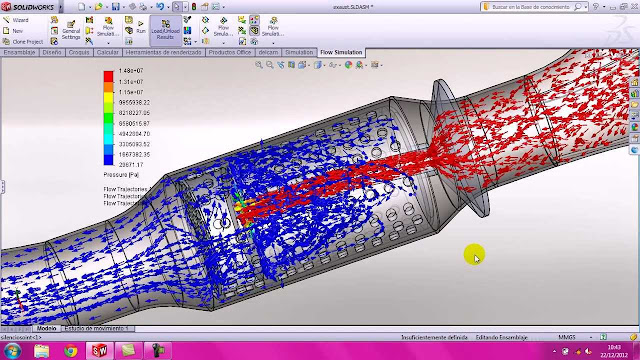
Brake System Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis
Please read previous blogs for introduction, concept, types of brake, hydraulic system, design review and component calculation for vehicle level parameters.
DFMEA – It is first step of
design process. DFMEA is a step-by-step approach for
identifying all possible failures in a design, a manufacturing or an assembly
process or a product or service.
Severity: How sever the issue is
on scale 1 to 10
1-
Not at all Severe ( No effect on
performance, durability, rules and regulation)
10- Most Dangerous (Life Threat, rule
violation or removal from Racing Competition)
Occurrence – Likelihood of this
event
1-
Not occur normally ( Example :
Steering Wheel wear)
10-
High chances of occurrence ( Example : Tyre wear)
Detection- Even after all
simulation and physical test, we can’t detect its chances
1-
Easily Detected by simulation and physical tests
10- Cannot be detected even after completing
all physical tests
Risk Priority Number: Change
Design if RPN > 100, RPN = Severity X Occurrence X Detection
Brake DFMEA:-
NO
|
ITEM/
FUNCTION
|
POTENTIAL
FAILURE MODE
|
POTENTIAL
EFFECT
OF FAILURE |
SEVERITY
|
POTENTIAL
CAUSES
|
OCCURANCE
|
CURRENT
DESIGN CONTROLS
|
DETECTION
|
RPN
|
|
PREVENTION
|
DETECTION
|
|||||||||
1
|
BRAKE
FLUID FLOW FROM BRAKE PIPE TO BRAKE CALIPERS
|
Leakage
or breakage at brake pipe or joints
|
Brake
Completely Fail
|
10
|
Wrong
Selection of material, Wrong End Joint Dimension,
Mismatch
in Brake Pipe and Master Cylinder / Calipers Thread
|
2
|
Simulation
for Burst Pressure, Stress and Strain.
Design
Calculation for Flared Thread Dimension
|
Material
Test, Dimension Measurement,
Burst
Pressure Measurement,
100%
Part Leak Test for 200 Bar for 30 Second
|
2
|
10*2*2=
40 |
Brake
Partially Fail
(
Fluid Pressure Drop)
|
10
|
|||||||||
2
|
BRAKE PAD
|
WEAR
RATE IS TOO HIGH
|
High
Braking Distance
|
9
|
Wrong
Selection of Pad or Disc material,
Wrong
Size of Pad or Disc,
Uneven
Pad wear
|
2
|
Pad
Heat Loss Simulation, Hand Calculation of brake pad and disc size
|
Disc/Pad
Corrosion Test +
Wear
Rate Measurement + Heat Generated Measurement,
Braking
Distance Test
|
2
|
9*2*2
=36
|
Braking Noise
|
5
|
2
|
5*2*2
=20
|
|||||||
3
|
BRAKE PEDAL
|
Brake
|
Brake Completely Fail
|
10
|
Wrong
Material, Low Strength of Pedal
|
2
|
Simulation
of Stress and Strain
|
Pedal
Braking Torque Test, Material Test
|
2
|
10*2*2
=40
|
High
Displacement
|
Driver Exhausted and Tired
|
7
|
Wrong
Pedal Lever Ratio, Wrong Master Cylinder Dia/Calipers Piston Size
|
3
|
Optimize
Master Cylinder/ Calipers Size, Optimize Actual vs. Optimal Braking Force
|
Ergonomic Check,
Static Braking Test, Continuous Braking
Test,
|
3
|
7*3*3
=63
|
||
Hard
Pressing
|
8
|
5
|
3
|
8*5*3
=120
|
||||||
Recommendation based on above DFMEA
NO
|
ITEM/
FUNCTION
|
RECOMMENDED
ACTION |
|
1
|
BRAKE FLUID FLOW FROM BRAKE PIPE TO BRAKE CALIPERS
|
1) Follow one
Norm for Thread European or American or Japanese
2) Have Better Factor for Safety by using CU-Ni Alloy |
|
2
|
BRAKE PAD
|
1) Use Carbon
Sintered Pad and Disc which has low wear rate.
2) place calipers
properly for even wear at pad
|
|
3
|
BRAKE PEDAL
|
Use Aluminum
Alloy Molding to eliminate welding and high strength, light weight Pedal
|
|
Optimize Pedal
Level Ratio for different Master
Cylinder Dia and Calipers Dia
|
|||