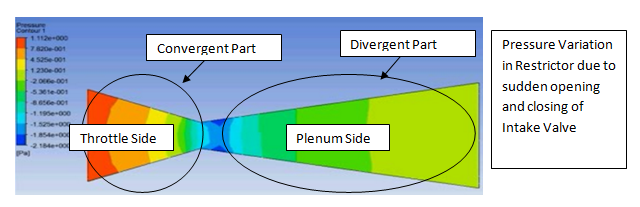
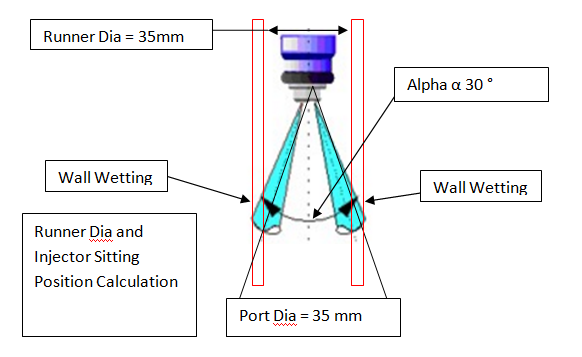
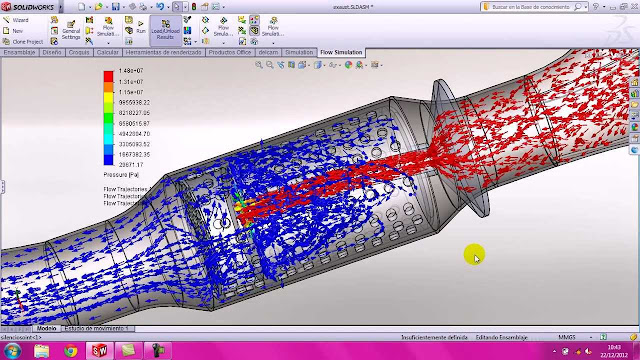
Brake System Design Review and DFMEA
Please read previous blog for vehicle static weight, center of gravity, engine, transmission etc.
Please read previous for following -
Different Types of Weight of Car, front and real calipers, Brake Pad, Brake Fluid Volume, front to rear weight bias, rear traction, lower polar moment of rotation, Skid, Tyre Thread Design, Car Center of Gravity and many more technical terms.
Below is only summary of design review done and explained in previous blog :-
|
Child Part
|
Requirement
|
Material
|
Manufacturing
|
Cost
|
Weight
|
Life
|
Design Review
|
|
Brake
Pipe
|
Burst Pressure =200
Bar Min
OD= 10mm Max ID=5mm Min Factor of Safety 5 Min |
Steel
Pipe
|
Multi
layer Seamless Piping with flared end
|
A
|
B
|
B
|
Ni- Alloy Brake pipe
is safe and have good life.
Ni- Alloy has higher Ultimate Tensile Strength so less material thickness pipe can be used. For same burst Pressure weight of Ni Apply pipe is least. |
|
Cu
Alloy
|
B
|
B
|
A
|
||||
|
Cu Ni Alloy *
|
C
|
A
|
A
|
||||
|
Brake
Oil
|
No Compressibility,
Anti Hygroscopic, High Dry/Wet Boiling Point, Fix Viscosity |
Silicone-based
|
Chemical
Process
|
B
|
/
|
B
|
Anti Hygroscope
property is better for glycol based fluid because water does not mix in
it. Glycol based fluid will be used in
brake.
|
|
¤ Glycol Based
|
B
|
/
|
A
|
||||
|
Disc
|
Mean Effective Radios
= 250mm,
Thickness = 20 mm Weight = 2 Kg Max |
Grey
Iron
|
Casting
|
A
|
C
|
B
|
Grey Iron is very
heavy and chances of rust are high. Siliconized carbon is very costly.
Reinforced Carbon will be used for Disc as it has long life and safe. |
|
Siliconized
carbon
|
Sintering
|
C
|
A
|
A
|
|||
|
^Reinforced Carbon
|
Sintering
|
B
|
A
|
A
|
|||
|
Piston
|
Dia =45mm,
Burst Pressure = 200 Bar |
Steel
|
Casting/Machining
|
A
|
C
|
B
|
Aluminum (ADC12) has
lesser weight so Al Piston will be used. (HPDC: high Pressure Die Casting)
|
|
Titanium
|
Casting/Machining
|
C
|
A
|
A
|
|||
|
ADC12#
|
HPDC,
Machining
|
B
|
B
|
B
|
|||
|
Master
Cylinder
|
Bore =10mm, Capacity =
15cc, Burst Pressure = 200 Bar
|
Steel
|
Casting/Machining
|
A
|
C
|
B
|
Aluminum (ADC12) has
lesser weight so Al Piston will be used.
|
|
ADC12#
|
HPDC,
M/c
|
B
|
A
|
B
|
|||
|
Brake
Pad
|
Area =50Cm2
Depth =40mm Thickness =15mm |
Ceramic
|
Sintering
|
B
|
A
|
B
|
Carbon Steel Pads will
be used as it has longer life and lesser cost.
|
|
¥Carbon Steel
|
Machining
|
B
|
B
|
A
|
|||
|
Brake
Pedal
|
Level Length =300mm
Pedal Area = 50X50mm2 |
Steel
|
Bending,
Welding
|
B
|
B
|
A
|
Cost reduction through
elimination of fixturing alignment, welding, and finishing operations required
for the welded steel assembly. so Al will be used
|
|
Al B356 T6
|
LPDC,
M/c
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
|||
|
Brake
Pressure Sensor
|
Pressure Voltage 0Bar 0V to 250Bar 5V
Accuracy = 1% |
Piezoelectric
|
Electronic
Chip Molding
|
/
|
/
|
/
|
Piezoelectric has
better sensitivity and responsiveness.
Twisted Wire Sensor will be used to avoid electronic noise.
|
|
Piezoresistive
|
/
|
/
|
/
|
||||
|
Hand
Brake Lever
|
Length =300mm
Handle Dia = 20mm Weight = 1Kg Max No Sharp Edge |
PA66
GF35
|
Molding
|
C
|
A
|
B
|
Steel will be used for
hand brake lever. Separate PA66 GF35 made handle can be assemble on Lever for
superior grip.
|
|
Aluminum
|
HPDC,
M/c
|
B
|
B
|
A
|
|||
|
Steel
|
Casting,
M/c
|
A
|
C
|
A
|
|||
|
Hand
Brake Cable Wire
|
Braiding Angle,
Ductility, Cable Dia/Wire Dia, Length, Elongation, Hardness
|
Cross
Braided Wire
|
Drawing,
Knitting
|
C
|
B
|
A
|
Spiral Braided Wire
will be used as its cost is less. Knitted Wire has more strength and life but
very costly.
|
|
€ Spiral Braided Wire
|
Drawing,
Twisting
|
A
|
B
|
B
|
(A: Best, B: Good, C: Average; M/c:
Machining; HPDC: High Pressure Die Casting)
(*Lipowsky & Arpaci, 2008, p.125), (¤ CDX Automotive, 2012, p.30), (¥ Elmarakbi,
2013, ch.16.8.1), (#Wan Hu, 2016), (€ Stapleton, Vizard and Sprinzel, 2008), (^Gilles, 2005, p.165)
Design Failure Mode Effect Analysis:
I have explained Severity rating, occurrence rating and detection in past in blogs of Intake DFMEA, Throttle DFMEA, Exhaust DFMEA.
- Severity, which rates the severity of the potential effect of the failure.
- Occurrence, which rates the likelihood that the failure will occur.
- Detection, which rates the likelihood that the problem will be detected before it reaches the end-user/customer.
Formula: The Risk Priority Number, or RPN, is a numeric assessment of risk assigned to a process, or steps in a process, as part of Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA), in which a team assigns each failure mode numeric values that quantify likelihood of occurrence, likelihood of detection, and severity of impact.
|
NO
|
ITEM/
FUNCTION
|
POTENTIAL
FAILURE MODE
|
POTENTIAL
EFFECT
OF FAILURE |
SEVERITY
|
POTENTIAL
CAUSES
|
OCCURANCE
|
CURRENT
DESIGN CONTROLS
|
DETECTION
|
RPN
|
|
|
PREVENTION
|
DETECTION
|
|||||||||
|
1
|
BRAKE
FLUID FLOW FROM BRAKE PIPE TO BRAKE CALIPERS
|
Leakage
or breakage at brake pipe or joints
|
Brake
Completely Fail
|
10
|
Wrong
Selection of material, Wrong End Joint Dimension,
Mismatch
in Brake Pipe and Master Cylinder / Calipers Thread
|
2
|
Simulation
for Burst Pressure, Stress and Strain.
Design
Calculation for Flared Thread
Dimension
|
Material
Test, Dimension Measurement,
Burst
Pressure Measurement,
100%
Part Leak Test for 200 Bar for 30 Second
|
2
|
10*2*2=
40 |
|
Brake
Partially Fail
(
Fluid Pressure Drop)
|
10
|
|||||||||
|
2
|
BRAKE PAD
|
WEAR
RATE IS TOO HIGH
|
High
Braking Distance
|
9
|
Wrong
Selection of Pad or Disc material,
Wrong
Size of Pad or Disc,
Uneven
Pad wear
|
2
|
Pad
Heat Loss Simulation, Hand Calculation of brake pad and disc size
|
Disc/Pad
Corrosion Test +
Wear
Rate Measurement + Heat Generated Measurement,
Braking
Distance Test
|
2
|
9*2*2
=36
|
|
Braking Noise
|
5
|
2
|
5*2*2
=20
|
|||||||
|
3
|
BRAKE PEDAL
|
Brake
|
Brake Completely Fail
|
10
|
Wrong
Material, Low Strength of Pedal
|
2
|
Simulation
of Stress and Strain
|
Pedal
Braking Torque Test, Material Test
|
2
|
10*2*2
=40
|
|
High
Displacement
|
Driver Exhausted and Tired
|
7
|
Wrong
Pedal Lever Ratio, Wrong Master Cylinder Dia/Calipers Piston Size
|
3
|
Optimize
Master Cylinder/ Calipers Size, Optimize Actual vs. Optimal Braking Force
|
Ergonomic Check,
Static Braking Test, Continuous Braking
Test,
|
3
|
7*3*3
=63
|
||
|
Hard
Pressing
|
8
|
5
|
3
|
8*5*3
=120
|
||||||
Based on above DFMEA following suggestions are made to improve brake system design
|
NO
|
ITEM/
FUNCTION
|
RECOMMENDED ACTION
|
|
|
1
|
BRAKE FLUID FLOW FROM BRAKE PIPE TO BRAKE CALIPERS
|
1) Follow one
Norm for Thread European or American or Japanese
2) Have Better Factor for Safety by using CU-Ni Alloy |
|
|
2
|
BRAKE PAD
|
1) Use Carbon
Sintered Pad and Disc which has low wear rate.
2) place calipers
properly for even wear at pad
|
|
|
3
|
BRAKE PEDAL
|
Use Aluminum
Alloy Molding to eliminate welding and high strength, light weight Pedal
|
|
|
Optimize Pedal
Level Ratio for different Master
Cylinder Dia and Calipers Dia
|
|||